What is LVM?
30 Aug 2021深入浅出讲述 Linux 上的 LVM (Logical Volume Manager 逻辑卷管理)
想象一个情况,我在网上买了个新电脑,自带 Windows 10 操作系统。512GiB 的硬盘我不想分区直接用,过了三个月:
它快满了,我就添置一块硬盘当仓库盘。但是有些文件太大我还要花时间移动到新的仓库盘上……

虽然现在传输速度很快,但是还要花时间查找能移动和不能移动的文件确实麻烦。所以现在隆重介绍 LVM 逻辑卷管理。
逻辑卷管理的重点在于 可以弹性调整 FlieSystem 的容量 而不是 注重文件传输效率和数据安全 上面。追求读写效率或者数据保护的可以使用 RAID 。
LVM 可以整合成多个物理硬盘在一起,让这些分区看起来像在一块大硬盘上。而且在将来还可以新增或者移除物理硬盘到 LVM 中。
什么是 LVM : PV, PE, VG, LV 的含义
LVM 全名 Logical Volume Manager ,大陆中文译作 逻辑卷管理。台湾中文翻译成 邏輯捲軸管理員。在这里我觉得用『捲軸』来解释更方便,引用一下鸟哥的解释:
之所以稱為『捲軸』可能是因為可以將 filesystem 像捲軸一樣伸長或縮短之故吧!
LVM 的做法是将几个实体的 Partitions分区 (或者 Disks硬盘) 通过软件转换成 LVM 最底层的 “块” (PV) ,然后将这些 “块” 组合成一块庞大的 “硬盘” (VG),接着将这块巨大的 “硬盘” 分割成一个个可以格式化的 “小硬盘” (LV),最终就能挂载使用了。但是为什么这样可以对 FileSystem 进行扩容和缩小呢?其实和一个叫 PE 的东西有关。
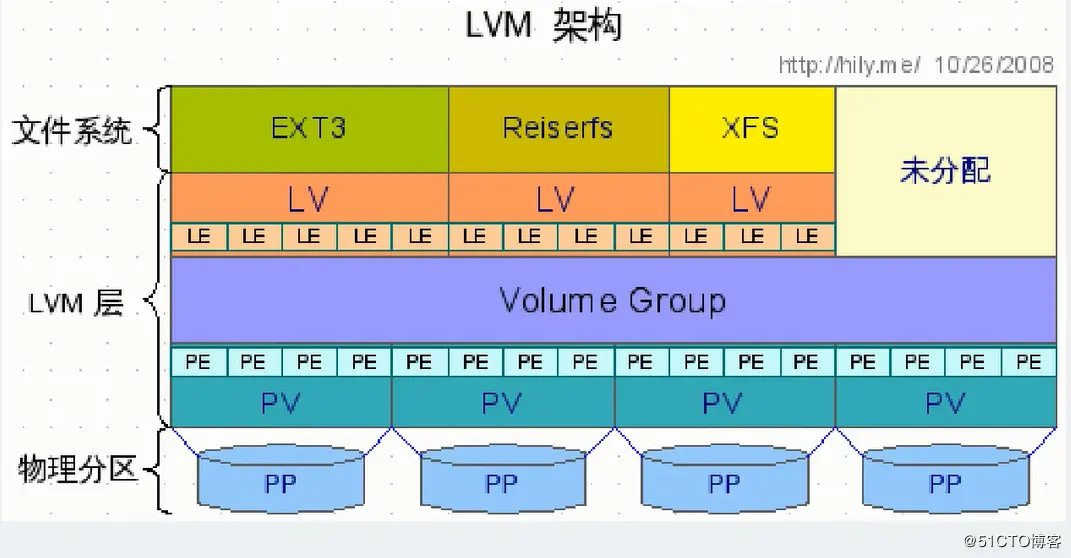
Physical Volume, PV, 物理卷
物理卷的理解其实很简单,可以近似看作是我们买来的实体的硬盘。但实际上物理卷(PV) 需要调整 硬盘(Disks)/分区(Partitions) 的 系统识别码(systemID) 为 8e( LVM 的识别码),然后再经过 pvcreate 的指令将它转换成 LVM 最底层的 物理卷(PV) ,之后才能将这些 PV 加以使用。调整 systemID 的方法有三种:gdisk, fdisk 和 parted。
注:gdisk是仅为GPT分区使用,fdisk是仅为MBR分区使用,如果用错的的话主引导记录会被清空,切记切记
Volume Group, VG, 卷组
顾名思义 卷组 就是很多个物理卷的凑成的一个组。就好比小学的时候会分小组,小组里面的每个同学就是物理卷,几个同学组成的一个组就是卷组。同理 VG 就是 LVM 将许多个 PV 整合成的东西。那么 VG 最大可以达到多少呢?这个和 PE物理块 和 LVM 的版本有关。在以前,32位的 Linux 操作系统上的 LVM(lvm1) 一个 LV 最大只能支持65534个 PE,假设使用 Linux 的默认设置(一个 PE 大小为4MiB),那么一个 LV 的最大容量也就只有 4M*65534/(1024M/G)=256GiB。不过在64位的操作系统上 LV 几乎不存在大小限制。(主要还是和寻址有关系)
Physical Extent, PE, 物理块
LVM 预设的 PE 大小是 4MiB。它是整个 LVM 的最小存储区块,换句话说就是我们写入的每个文件都是往 PE 里面填充的。简单来说 PE 很像在机械硬盘上划分的磁道。所以调整 PE 大小会影响到 LVM 的最大容量的。但是在 CentOS/Red Hat 6 之后的操作系统普遍采用 lvm2 技术,以及64位 CPU 的出现,因此这个限制不复存在。
Logical Volume, LV, 逻辑卷
最终 一大块 VG 会像切蛋糕一样分成一个个 LV ,这些被切出来的 LV 就是能吃的格式化使用的东西了。

那么问题来了:LV 可以随意划分大小吗?答案是不可以。因为 PE 是 LVM 中最小的存储单位,所以 LV 的大小和 PV 的块数相关。在 Linux 系统中,为了方便我们使用 LVM 管理磁盘,LV 通常被命名为 /dev/vg_name/lv_name 的样子。
此外,前文中提及到 LVM 可以弹性变更 FileSystem 的容量,实际上是通过 “交换PE” 来进行扩容和缩小的操作,将原本逻辑卷LV中的物理块PE移出以缩小容量,将空闲的物理块PE移入现有逻辑卷LV以扩容。如下图:
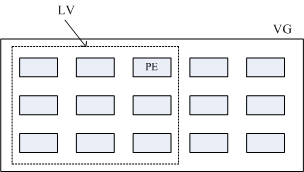
VG 内的 PE 会分给虚线部分的 LV ,如果未来这个 VG 要扩充的话,加上其他的 PV 即可。最重要的是如果 LV 要扩充的话,也可以通过加入 VG 内没有使用到的 PE 来扩充的。
Logical Extent, LE, 逻辑块
逻辑卷LV中可以分配的最小存储单元,在同一卷组VG中LE的大小和PE是相同的,并且一一相对。
LVM 工具
fdisk, gdisk 和 parted
- fdisk
[student@node2 ~]## fdisk /dev/sda
欢迎使用 fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2)。
更改将停留在内存中,直到您决定将更改写入磁盘。
使用写入命令前请三思。
命令(输入 m 获取帮助): <==这里可以输入指令,可以按 m 来查看所有指令
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):m
命令操作
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition #删除一个分区
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition #增加一个新分区
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table #打印分区表
q quit without saving changes #不储存直接离开
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit #写入分区表并离开
x extra functionality (experts only)
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):
- gdisk
[student@node2 ~]# gdisk /dev/vda <==仔細看,不要加上數字喔!
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.6
Partition table scan:
MBR: protective
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: present
Found valid GPT with protective MBR; using GPT. <==找到了 GPT 的分割表!
Command (? for help): <==这里可以输入指令,可以按 ? 来查看所有指令
Command (? for help): ?
b back up GPT data to a file
c change a partition's name
d delete a partition #删除一个分区
i show detailed information on a partition
l list known partition types
n add a new partition #增加一个新分区
o create a new empty GUID partition table (GPT)
p print the partition table #打印分区表
q quit without saving changes #不储存直接离开
r recovery and transformation options (experts only)
s sort partitions
t change a partition's type code
v verify disk
w write table to disk and exit #写入分区表并离开
x extra functionality (experts only)
? print this menu
Command (? for help):
- parted
[student@node2 ~]# parted /dev/sda
GNU Parted 3.1
使用 /dev/sda
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
(parted) help
align-check TYPE N check partition N for TYPE(min|opt) alignment
help [COMMAND] print general help, or help on COMMAND
mklabel,mktable LABEL-TYPE create a new disklabel (partition table)
mkpart PART-TYPE [FS-TYPE] START END make a partition
name NUMBER NAME name partition NUMBER as NAME
print [devices|free|list,all|NUMBER] display the partition table, available devices, free space, all found partitions, or a particular partition
quit exit program
rescue START END rescue a lost partition near START and END
resizepart NUMBER END resize partition NUMBER
rm NUMBER delete partition NUMBER
select DEVICE choose the device to edit
disk_set FLAG STATE change the FLAG on selected device
disk_toggle [FLAG] toggle the state of FLAG on selected device
set NUMBER FLAG STATE change the FLAG on partition NUMBER
toggle [NUMBER [FLAG]] toggle the state of FLAG on partition NUMBER
unit UNIT set the default unit to UNIT
version display the version number and copyright information of GNU Parted
(parted)
PV 阶段
- pvcreate :将实体partition 建立成为 PV ;
- pvscan :搜寻目前系统里面任何具有 PV 的磁盘;
- pvdisplay :显示出目前系统上面的 PV 状态;
- pvremove :将 PV 属性移除,让该partition 不具有PV 属性。
VG 阶段
- vgcreate :就是主要建立 VG 的指令;
- vgscan :搜寻系统上面是否有 VG 存在;
- vgdisplay :显示目前系统上面的 VG 状态;
- vgextend :在 VG 内增加额外的 PV ;
- vgreduce :在 VG 内移除 PV ;
- vgchange :设定 VG 是否启动(active);
- vgremove :删除一个 VG 。
LV 阶段
- lvcreate :建立 LV ;
- lvscan :查询系统上面的 LV ;
- lvdisplay :显示系统上面的 LV 状态;
- lvextend :在 LV 里面增加容量;
- lvreduce :在 LV 里面减少容量;
- lvremove :删除一个 LV ;
- lvresize :对 LV 进行容量大小的调整。
LVM 实操流程
在这里我们就用 RHel 8 RH134 的题目来演练一下如何调整逻辑卷大小以及创建逻辑卷。
十六、调整逻辑卷大小
1)预先创建 2GiB 的分区/dev/vdb1,并用于创建卷组 testvg
2)创建大小为 200MiB 的逻辑卷/dev/testvg/vo,格式化为 xfs 文件系统,并挂载在/mnt/vo 上
3)将逻辑卷/dev/testvg/vo 及其文件系统大小调整到 300MiB,确保文件系统内容保持不变。
[student@node2 ~]# fdisk /dev/vdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.32.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xae75bf0a.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p):
Using default response p.
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
First sector (2048-10485759, default 2048):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-10485759,default 10485759): +2G
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 2 GiB.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[student@node2 ~]# pvcreate /dev/vdb1
[student@node2 ~]# vgcreate testvg /dev/vdb1
[student@node2 ~]# lvcreate -L 200M -n vo testvg
[student@node2 ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/testvg/vo
[student@node2 ~]# mkdir /mnt/vo
[student@node2 ~]# vim /etc/fstab
/dev/testvg/vo /mnt/vo xfs defaults 0 0
[student@node2 ~]# mount -a
[student@node2 ~]# df -hT /dev/testvg/vo # 查看文件系统的类型
和大小
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/testvg-vo xfs 195M 12M 183M 6% /mnt/vo
[student@node2 ~]# lvextend -L 300M /dev/testvg/vo
[student@node2 ~]# lvs
LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync
Convert
vo testvg -wi-ao---- 300.00m
# 扩展文件系统,ext 类型的文件系统用 resize2fs /dev/testvg/vo,后面接的是逻辑卷的路径。
[student@node2 ~]# xfs_growfs /mnt/vo # 后面接的是挂载点的路径
[student@node2 ~]# df -hT /dev/testvg/vo
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/testvg-vo xfs 295M 13M 283M 5% /mnt/vo
十八、创建逻辑卷
根据以下要求,创建新的逻辑卷:
1)逻辑卷的名字为 mylv,属于 myvg 卷组,大小为 50 个 pe
2)卷组 myvg 中的逻辑卷的 pe 大小应当为 16MiB
3)使用 vfat 文件系统将逻辑卷 mylv 格式化
4)此逻辑卷应当在系统启动时自动挂载到/mnt/mydata 目录下
[student@node2 ~]# fdisk /dev/vdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.32.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p):
Using default response p.
Partition number (3,4, default 3):
First sector (5244928-10485759, default 5244928):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (5244928-10485759,default 10485759):
+1G
Created a new partition 3 of type 'Linux' and of size 1 GiB.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Syncing disks.
[student@node2 ~]# pvcreate /dev/vdb3
[student@node2 ~]# vgcreate -s 16M myvg /dev/vdb3
[student@node2 ~]# lvcreate -l 50 -n mylv myvg
[student@node2 ~]# mkfs.vfat /dev/myvg/mylv
[student@node2 ~]# mkdir /mnt/mydata
[student@node2 ~]# vim /etc/fstab
/dev/myvg/mylv /mnt/mydata vfat defaults 0 0
[student@node2 ~]# mount -a
[student@node2 ~]# df -h /mnt/mydata/
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/myvg/mylv 799M 4.0K 799M 1% /mnt/mydata